Environmental Sustainability Within Private Companies
Environmental sustainability has become a major concern for private companies worldwide following the Paris Agreement. A cross-regional analysis of the changing landscape of environmental sustainability within private companies in the European Union, the United States, and China.
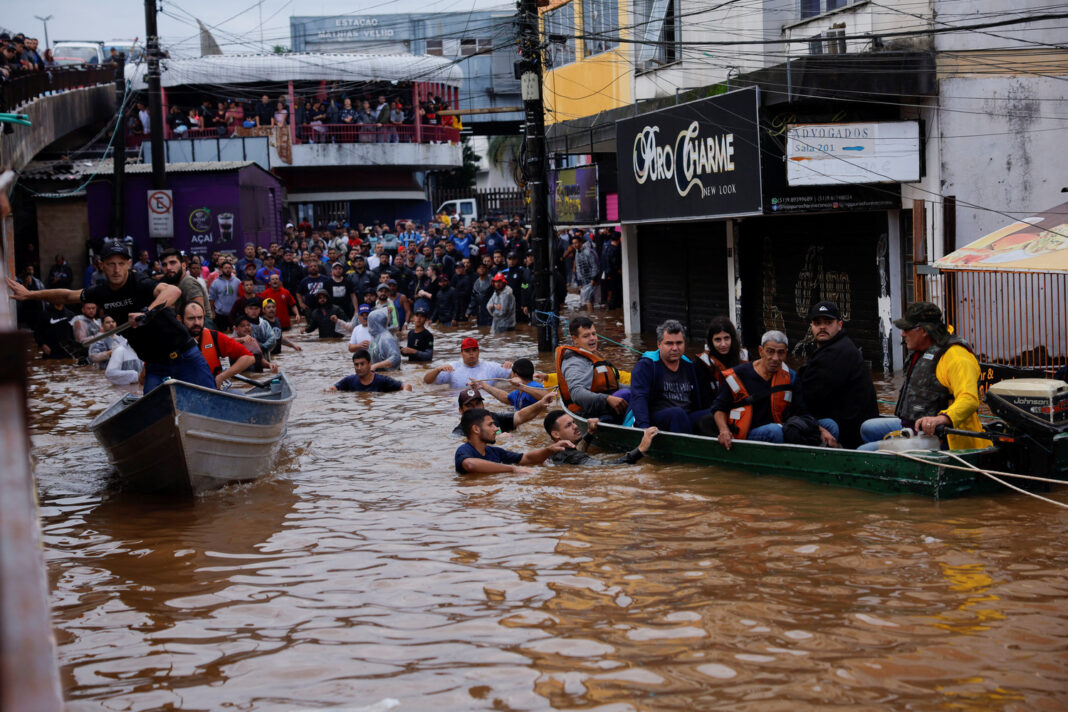

The European Union's recent ratification of the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) marks a significant step towards fostering environmental sustainability within the private sector. The CSRD, as a mandatory implementation from January 2024, imposes stricter rules on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting, thereby enhancing accountability and transparency across European businesses.
Siemens Healthineers, a leading German global corporation, serves as an exemplar of how the CSRD is reshaping private enterprises within the EU. With its ambitious goals of reaching 250 million underserved patients and providing 6 million hours of training to medical professionals, Siemens Healthineers exemplifies a commitment to sustainability and social responsibility. By aligning its objectives with the principles of the CSRD, Siemens Healthineers showcases how corporate adaptation strategies can positively impact both business development and societal well-being.
The implementation of the CSRD is not only a regulatory requirement but also a strategic imperative for companies operating within the EU. By integrating sustainability into their core business processes, companies like Siemens Healthineers not only enhance their reputation but also drive long-term value creation. The correlation between adherence to the CSRD and improved business performance underscores the importance of environmental sustainability in shaping the contemporary business landscape.
Conversely, on one side of the world, being the world’s largest annual greenhouse gas emitter, China’s responsibility to call for sustainable development within domestic companies remains incontrovertible. Following the ratification of the Paris Agreement, China’s most recent legislative developments increasingly focus on ESG principles which are largely driven by governmental policies.
In 2023, the China Enterprise Reform and Development Society (CERDS) released voluntary guidelines for ESG reporting. While significant cases inter alia company’s illegal discharge of pollutants into the Yellow River still occur, pioneers like Xinyi Solar Holdings, a Hong Kong based solar glass manufacturer and supplier, which mainly operates in mainland China has been on the forefront of sustainable development with their eighth “Environmental, Social and Governance Report'' henceforth. Xinyi Solar’s compliance with international environmental standards predominantly derives from its commitment to effective environmental management systems (EMS) and by regularly executing Environmental Impacts Assessments (EIAs) to identify potential (environmental) risks and thus develop strategies to mitigate them.
On the other extreme of the world, the United States has a comprehensive legal framework for environmental sustainability, mainly developed during the 1970s. The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a central role thanks to its mandate to protect public health and the environment by enforcing acts approved by the US Congress. Since the early 1990s, the EPA has been developing a program called Safer Choice to help consumers and businesses choose safer products for human health and the environment. The Safer Choice program is not an act approved by Congress, however it operates under several federal acts such as the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) and the Pollution Prevention Act (PPA).
Apple, for instance, as one of the Safer Choice Partners, is dedicated to protecting the people in its supply chain and customers by using safer chemicals in its manufacturing processes. According to its 2024 Annual Progress Report, 22% of Apple products were made from recycled or renewable sources. Furthermore, Apple is committed to achieving zero net emissions across its entire carbon footprint by 2030, demonstrating its dedication to the planet.
In conclusion, despite differences in approach, the EU, US, and China are all fostering ESG objectives. While recent reaffirmation of the US commitment to the Paris Agreement with President Biden underlines the US willingness to not be left behind; companies like Siemens Healthineers serve as catalysts of progress, demonstrating how adherence to sustainability standards can drive innovation, competitiveness, and societal impact, whereas China’s motivation to achieve sustainability derives from a different cultural context and thus the economic priority to establish “common prosperity” outweighs the government’s objective to strictly implement standardized ESG legislation for the majority of its companies.